How Trading Pairs Shape Arbitrage Opportunities in Crypto Markets
When you trade Bitcoin for Ethereum on Binance, or swap USDT for SOL on KuCoin, you're not just buying or selling-you're interacting with a trading pair. These pairs aren’t just labels. They’re the invisible architecture that makes arbitrage possible. And in crypto, where prices jump seconds after you click buy, understanding how trading pairs work can mean the difference between profit and loss.
What Trading Pairs Actually Do
A trading pair is simply two assets that can be exchanged for each other. BTC/USDT means you’re trading Bitcoin for Tether. ETH/BTC means you’re trading Ethereum for Bitcoin. On its surface, it’s straightforward. But underneath, each pair creates a price relationship that other traders watch like hawks. Arbitrage happens when the same asset trades at different prices across markets. If BTC is $62,000 on Binance and $62,150 on Bybit, you can buy low, sell high, and pocket the $150. Simple, right? But here’s the catch: that $150 doesn’t exist in a vacuum. It only exists because of the trading pair structure. If Binance didn’t list BTC/USDT and Bybit didn’t list the same pair, there’d be no direct comparison. No arbitrage. Trading pairs create the bridge between markets. They define what’s being measured, and how. Without them, price discrepancies are invisible.Exchange Arbitrage: The Low-Hanging Fruit
The most common form of arbitrage in crypto is exchange arbitrage. It’s the same asset, different exchanges, different prices. This is where trading pairs become your roadmap. Say you’re watching BTC/USDT across five exchanges. One has it at $61,800. Another at $62,200. The spread is $400. After fees, slippage, and withdrawal delays, you’re left with maybe $250 profit. But you need to act fast-these gaps close in under 10 seconds. This isn’t something you do manually. Traders use bots that monitor dozens of pairs across multiple exchanges in real time. These bots scan for price mismatches, calculate net profit after fees, and execute trades before the market adjusts. The more trading pairs you track, the more opportunities you see. But here’s what most beginners miss: not all pairs are equal. BTC/USDT is liquid. So is ETH/USDT. But what about SHIB/BTC? That pair has thin order books. A $100 trade might move the price by 5%. That’s not arbitrage-that’s gambling. Stick to pairs with high volume and tight spreads. That’s where the real opportunities live.Triangular Arbitrage: The Hidden Matrix
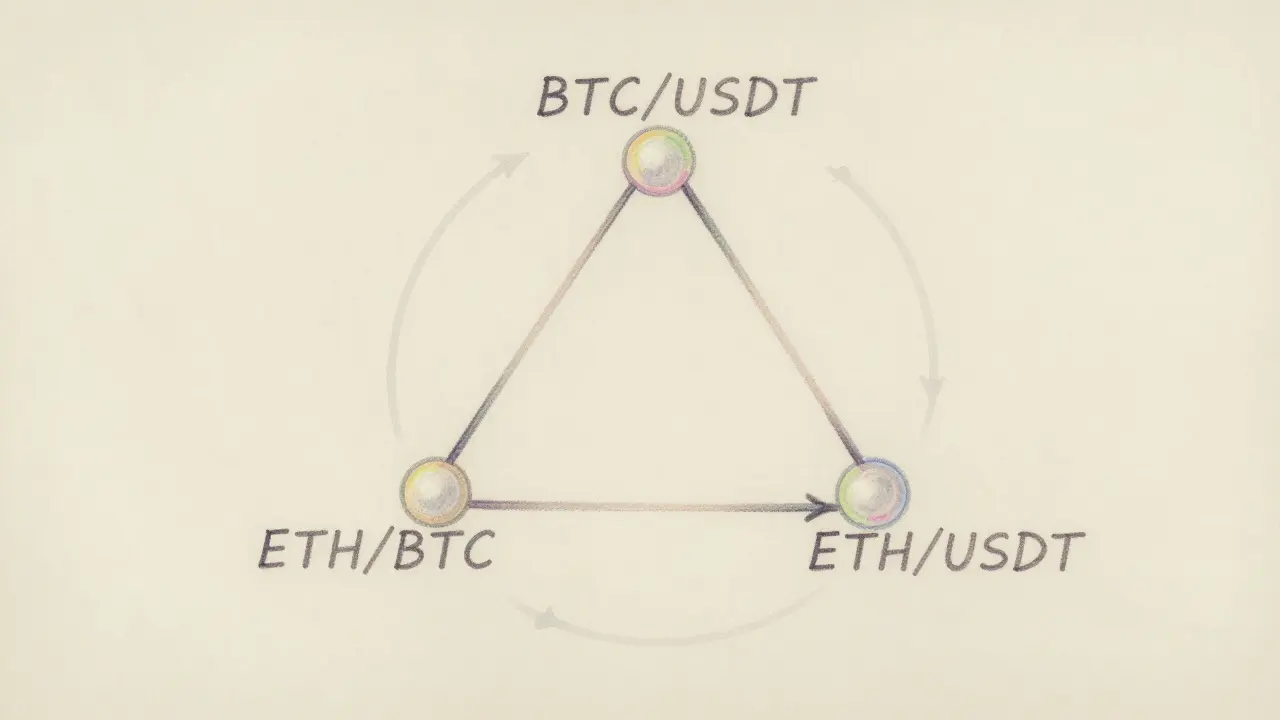
Now imagine you’re on a single exchange-say, Binance. You notice something odd. BTC/USDT is $62,000. ETH/BTC is 0.048. ETH/USDT is $2,970. Let’s do the math: - Start with $10,000 in USDT - Buy ETH: $10,000 / $2,970 = 3.367 ETH - Buy BTC: 3.367 ETH * 0.048 = 0.1616 BTC - Sell BTC: 0.1616 BTC * $62,000 = $10,019.20 You turned $10,000 into $10,019.20. That’s a 0.19% profit. Sounds tiny? Multiply that by $1 million trades, and you’re talking $1,900 per cycle. Do it 10 times a minute? That’s $114,000 an hour. That’s triangular arbitrage. And it only works because of the three trading pairs: BTC/USDT, ETH/BTC, ETH/USDT. They form a triangle. If the math doesn’t add up, you’ve found an arbitrage window. But here’s the problem: exchanges know this. Most have anti-arbitrage measures built into their systems. The window closes in milliseconds. You need low-latency API access, co-located servers, and a bot that can execute in under 200ms. This isn’t for hobbyists. It’s for teams with engineering resources. But it’s real. And it’s happening right now on major exchanges.Pairs Trading: When Crypto Gets Serious
If you think arbitrage is only about buying low and selling high, you’re missing the bigger picture. There’s another type-pairs trading-that’s been used on Wall Street for decades and is now creeping into crypto. Pairs trading isn’t about one asset being mispriced. It’s about two assets that usually move together suddenly drifting apart. Example: BTC and ETH have historically moved in sync. When BTC goes up 5%, ETH usually goes up 6%. But one day, BTC rises 5% while ETH only goes up 1%. That’s a divergence. A signal. A pairs trader would short ETH and go long BTC, betting that ETH will catch up. If the relationship reverts-which it usually does-they close both positions and pocket the difference. This works because of something called cointegration. It’s a statistical test that shows two assets share a long-term relationship, even if they diverge short-term. You don’t need to predict the market. You just need to know when the bond between two assets is broken. In crypto, this works best with stablecoin pairs: USDT/USDC, WBTC/renBTC, or even ETH/LINK. These aren’t random pairs. They’re similar assets with similar use cases. When their price ratio drifts, it’s usually temporary. The advantage? You’re not betting on whether crypto goes up or down. You’re betting on the relationship between two things. That’s a hedge. It works in bull and bear markets.Decentralized Arbitrage: The AMM Wild West
Centralized exchanges use order books. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) like Uniswap and SushiSwap use automated market makers (AMMs). These rely on liquidity pools. If someone buys a lot of ETH from the ETH/USDT pool, the price of ETH in that pool rises. But here’s the gap: the price on Uniswap might be $3,000, while on Coinbase it’s $2,980. That’s an arbitrage opportunity. Traders use flash loans-borrowing millions in crypto without collateral-to exploit this. They borrow $5 million in USDT, swap it for ETH on Uniswap, sell that ETH on Coinbase, repay the loan, and keep the profit. All in one transaction. No upfront capital needed. This is where trading pairs become even more critical. Because AMMs price assets based on ratios inside pools, the pair structure determines how sensitive the price is to trades. A pair with $10 million in liquidity won’t move much. A pair with $100,000? One big trade can swing the price 10%. That’s why arbitrageurs monitor liquidity levels alongside price. They don’t just look for price gaps-they look for exploitable gaps.
Why Most People Lose at Arbitrage
You see YouTube videos: “Make $500/day with crypto arbitrage!” Sounds easy. But here’s the reality: - Fees eat 0.1-0.5% per trade. Two trades? That’s 1% gone before you even start. - Withdrawal delays can kill a trade. If your BTC takes 20 minutes to move from Binance to Bybit, the price gap is long gone. - Slippage on thin pairs turns profit into loss. - Most bots are overpriced junk. Many are scams. - Exchange withdrawal limits cap your size. You can’t scale. The real edge isn’t finding opportunities. It’s execution speed, cost control, and risk management. The best arbitrageurs don’t chase every gap. They wait for the ones with high volume, low fees, and tight spreads. They know that 95% of opportunities are illusions.What You Can Actually Do Today
You don’t need a $500,000 bot to get started. Here’s how to begin:- Start with one pair: BTC/USDT. Track it on two exchanges you already use.
- Use free tools like TradingView or CoinGecko to compare prices.
- Calculate fees: deposit, withdrawal, trading. If the spread is less than 1.5%, it’s not worth it.
- Try triangular arbitrage on one exchange. Use a calculator. See if the math adds up after fees.
- Watch BTC and ETH over a week. Do their price ratios stay stable? If not, you’ve found a pairs trading candidate.
Final Thought: The Market Isn’t Efficient-But It’s Getting Faster
Crypto markets aren’t perfectly efficient. That’s why arbitrage exists. But they’re getting smarter. Bots are everywhere. Liquidity is deeper. Gaps close faster. The traders who win aren’t the ones who spot the biggest spread. They’re the ones who understand the structure behind it. Who know which pairs matter, which ones are traps, and how to move before the crowd. If you want to profit from arbitrage, stop chasing quick wins. Start studying trading pairs. Learn how they connect. Watch how they behave. The profit isn’t in the price difference. It’s in the pattern.Can you make money with crypto arbitrage today?
Yes, but not easily. The easy opportunities are gone. Profitable arbitrage now requires fast execution, low fees, and deep understanding of trading pair dynamics. Most retail traders lose money due to fees, delays, and poor pair selection. Success comes from focusing on high-volume pairs, automating trades, and managing risk-not chasing every price gap.
What’s the difference between exchange arbitrage and triangular arbitrage?
Exchange arbitrage involves buying an asset on one exchange and selling it on another where the price is higher-like buying BTC on Binance and selling it on KuCoin. Triangular arbitrage happens within a single exchange and uses three trading pairs to create a profit loop. For example: USDT → ETH → BTC → USDT. If the final amount of USDT is more than you started with, you made a profit. Triangular arbitrage is faster but requires precise math and low-latency execution.
Do I need a bot to do arbitrage?
You don’t need one, but you’ll lose without it. Manual arbitrage is nearly impossible in crypto because price gaps close in seconds. Bots monitor dozens of pairs across multiple exchanges in real time and execute trades faster than any human. Even simple bots can be built with free tools like Python and TradingView alerts. If you’re serious, automation isn’t optional-it’s essential.
Why do some trading pairs have more arbitrage opportunities than others?
High-volume pairs like BTC/USDT, ETH/USDT, and SOL/USDT have tighter spreads and more liquidity, meaning price differences between exchanges are smaller and less frequent. Low-volume pairs like MEME tokens or obscure altcoins often have wider spreads-but they’re risky. A $1,000 trade can move the price 20%, wiping out your profit. The best opportunities are in liquid pairs with moderate spreads, not in volatile, illiquid ones.
Is pairs trading the same as arbitrage?
No, but they’re related. Arbitrage exploits immediate price differences between markets. Pairs trading exploits long-term relationships between two assets that usually move together. If BTC and ETH usually rise and fall in sync, but one falls while the other rises, you bet they’ll revert. It’s not instant profit-it’s statistical. It’s slower, less risky, and works even when markets are flat or falling.
Can flash loans make arbitrage risk-free?
No. Flash loans let you borrow money without collateral and repay it in the same transaction, which sounds risk-free. But if the trade fails-because of slippage, a smart contract bug, or a sudden price move-you still lose the gas fees. Plus, large flash loan attacks can trigger market-wide volatility. While powerful, they’re not a free lunch. They’re high-stakes, technical plays that require deep blockchain knowledge.





So you're telling me the whole crypto arbitrage thing is just fancy math with extra steps? I'm out.
Trading pairs aren't just bridges-they're the neural pathways of the crypto nervous system. The market isn't pricing assets, it's recalibrating relational entropy in real time. You're not trading BTC/USDT-you're mapping the topological distortion of liquidity fields across decentralized spacetime.
People still think arbitrage is about 'finding gaps'? Lol. The gaps are bait. The real game is watching who gets sucked in by low-volume meme pairs while the whales quietly reposition across BTC/USDT and ETH/USDT. You don't chase arbitrage-you engineer the conditions for it.
Triangular arbitrage? More like triangular delusion. The math works in theory, but in practice? Your bot gets front-run by the exchange’s own algo, your gas fees eat the profit, and you’re left wondering why your ‘risk-free’ trade just cost you $120 in ETH.
i just use binance and coinbase and check prices on my phone. if there's a 2% diff i buy and sell. no bot. no fancy math. just patience. sometimes it works.
One must consider the geopolitical undercurrents of trading pair liquidity. The dominance of USDT as a base pair is not accidental-it is a symptom of the centralized financial infrastructure’s encroachment into decentralized ecosystems. Are we truly free when our arbitrage is predicated on a fiat-pegged token controlled by a single entity?
There’s a quiet poetry in how trading pairs reveal the hidden architecture of value. BTC/USDT isn’t just a ticker-it’s a contract between trust and transparency. When the ratio wavers, it’s not a glitch-it’s a whisper from the market’s subconscious. The real arbitrage isn’t in the profit-it’s in the moment you realize you’re no longer trading assets, but narratives.
I’ve been watching BTC/ETH ratios for months now… and yes, they do revert-usually after a 12-hour lag, sometimes after a 3-day divergence… but here’s the thing: the reversion isn’t random, it’s rhythmic, like a heartbeat… and if you time your short/long just right, you don’t even need to predict the market-you just ride the wave… and yes, I’ve made 37% this year just doing that… no bots… just charts… and coffee… and too many spreadsheets…
The most overlooked factor in arbitrage is not speed or liquidity-it’s withdrawal timing. Many traders lose because they assume their funds will move instantly. In reality, Binance withdrawals can take 40 minutes during peak hours. That’s more than enough time for a $400 spread to vanish. Always test your withdrawal times before deploying capital.
This is actually one of the clearest breakdowns of crypto arbitrage I’ve read. I’ve been trying to wrap my head around this for months. The triangular arbitrage example with the math? Perfect. I’m going to try running a small test with $500 this weekend. Thanks for laying it out like this.
All this talk about pairs and bots is just a distraction. The real arbitrage is in the fact that 90% of retail traders are too lazy to learn basic math. The market isn’t efficient-it’s just full of people who think 'HODL' is a strategy. Wake up. The bots aren't the enemy. The laziness is.
you think this is about trading pairs? nah. the fed controls all the usdt. every price you see is rigged. they let you win small so you keep playing. the real money is in the dark pools where the big boys trade before the pairs even show up. you think you're arbitraging? you're just feeding the machine
why do people overcomplicate this. just buy low sell high. i did it with shiba and made 5k in a week. pairs? arbitrage? who cares. its all meme anyway
This is not merely a technical exercise-it is an epistemological inquiry into the nature of value in a post-fiat world. The trading pair is the dialectical tension between liquidity and perception, between algorithmic precision and human irrationality. To master arbitrage is to master the dance between order and chaos.
Let’s be honest-most of this is propaganda from people who run bot farms. The 'high-volume pairs' are the ones the exchanges promote to suck in retail. The real arbitrage is happening between CEX and DEX, and the only people who profit are the ones who control the liquidity pools. You’re not the hunter-you’re the prey.
Great breakdown. One thing I’d add: always check the depth chart before you trade. A $62,000 BTC/USDT price looks great-but if the buy wall is only $50k deep, your $10k order will move the price and kill your profit. Volume matters, but depth matters more.
America built this market. The rest of the world is just borrowing our infrastructure. USDT dominates because it’s backed by the dollar. If you’re trying to arbitrage on non-US exchanges, you’re playing with fire. Stick to the pairs that matter: USD-backed, regulated, liquid. Everything else is noise.
I read this whole thing and my brain hurt. I just buy ETH when it dips below $2,900 and sell when it hits $3,100. That’s my 'arbitrage'. No bots. No triangles. No flash loans. Just vibes and a little patience.
Arbitrage is dead. The only thing left is HODLing and pretending you're smart.